Answered By: Richard Directo Last Updated: Sep 06, 2023 Views: 675
Scopus is a source-neutral abstract and citation database curated by independent subject matter experts who are recognized leaders in their fields. Scopus puts powerful discovery and analytics tools in the hands of researchers, librarians, research managers and funders to promote ideas, people and institutions. Scopus indexes content from 7,000+ publishers and includes 91+ million records, 94,000+ affiliation profiles and 17+ million authors. Its state-of-the-art search tools and filters help uncover relevant information, monitor research trends, track newly published research and identify subject experts .Plus, its analytics tools make it easy to visualize, compare and export the data.
Accessing Scopus Database:
1. Go to CLR's website at https://clr.benilde.edu.ph/clr
2. Click on "A-Z databases list" button
3. In the A-Z databases list, click on letter "S" and look for "Scopus"
4. Log in using your InfoNet credentials (For students, it is your ID number)
Found below is the home page of Scopus:

5. Performing a document search.
- A. The Document search tab is the Scopus homepage. Other tabs are Author, Research Discovery and Affiliations.
- B. Enter your search terms in this field. You can combine multiple search terms within one field. Select which fields you wish to search from using the
dropdown menu. - C. Add search field and select Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) to combine search terms.
- D. Add date range to focus on particular publication periods.
- E. Your search history is shown here with the options to set alert, save or delete queries.

6. Working with document search results.
- A. Use the Refine search options to filter the results by subject area, document type, language, keyword, author, funding sponsor, etc.
- B. Click Analyze results for a breakdown of results by criteria including year, source, author, affiliation, territory, type, subject area, and funding sponsor.
- C. These options allow batch processing of all or selected results (export; download; view citation overview, view citing documents; save to list; view references; bibliography; or send results as
an email). - D. Sort results by date (default option), cited by, relevance, first author name or source title.
- E. Click Show abstract to display the abstract. View at Publisher opens the full text on the publisher website, if
authorized. Related documents displays referenced works.

6. Working with a document details page.
- From the search results, click your preferred document title to access the details page.

- A. Click an author name to go to the profile page for that author.
- B. Click Full text options then view at publisher to open the full text on the publisher’s website, if authorized.
- C. View the author keywords assigned and indexed keywords.
- D. View citation article level metrics, including PlumX Metrics, to evaluate both citation impact and levels of community engagement around an article.
- E. View the references cited in this document. The titles link to the abstract pages for those articles.
- F. View related documents (with shared references, authors, keywords and abstract).

7. Performing an author search and working with results.
- A. The Author search tab is beside the document search tab. Enter the last name and first name of the author in the
two author fields. Affiliation information can also be added in the Affiliation field. Scopus will display a list of possible matches. - B. You can also search for authors using their ORCID ID.

- Click the name of your selected author to open the author profile.
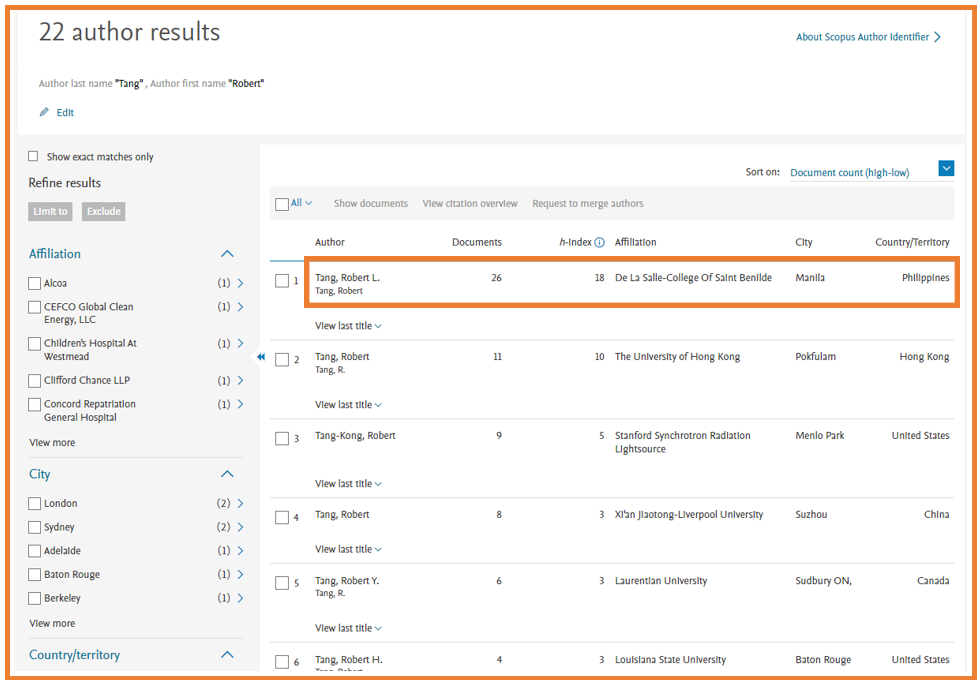
- A. Click View h-Graph to display the h-index as a graph.
- B. Click Analyze author output to visualize their output as graphs.
- C. View Citation overview analyzes citations of their articles by publication year.

To discover more e-resources in our collection which you can also access anytime, anywhere, please visit our A-Z list of databases.
RELATED FAQ:
How do I access online resources/databases on and off campus?
Was this helpful? 1 0
